Mining pushes equipment to its limits. Equipment runs long hours in dust, mud, and extreme temperatures, and when something breaks, production stops. Hydraulics play a huge role in keeping things running, powering everything from excavators and shovels to crushers and conveyors. But with that much power comes serious pressure on fittings, hoses, and connections. That’s where quality fittings and hose protection come into play. Let’s dig into how these systems work across the mining industry and the products that keep them performing day after day.
Digging Deeper: Fittings & Hose Protection at Work in The Mining Industry
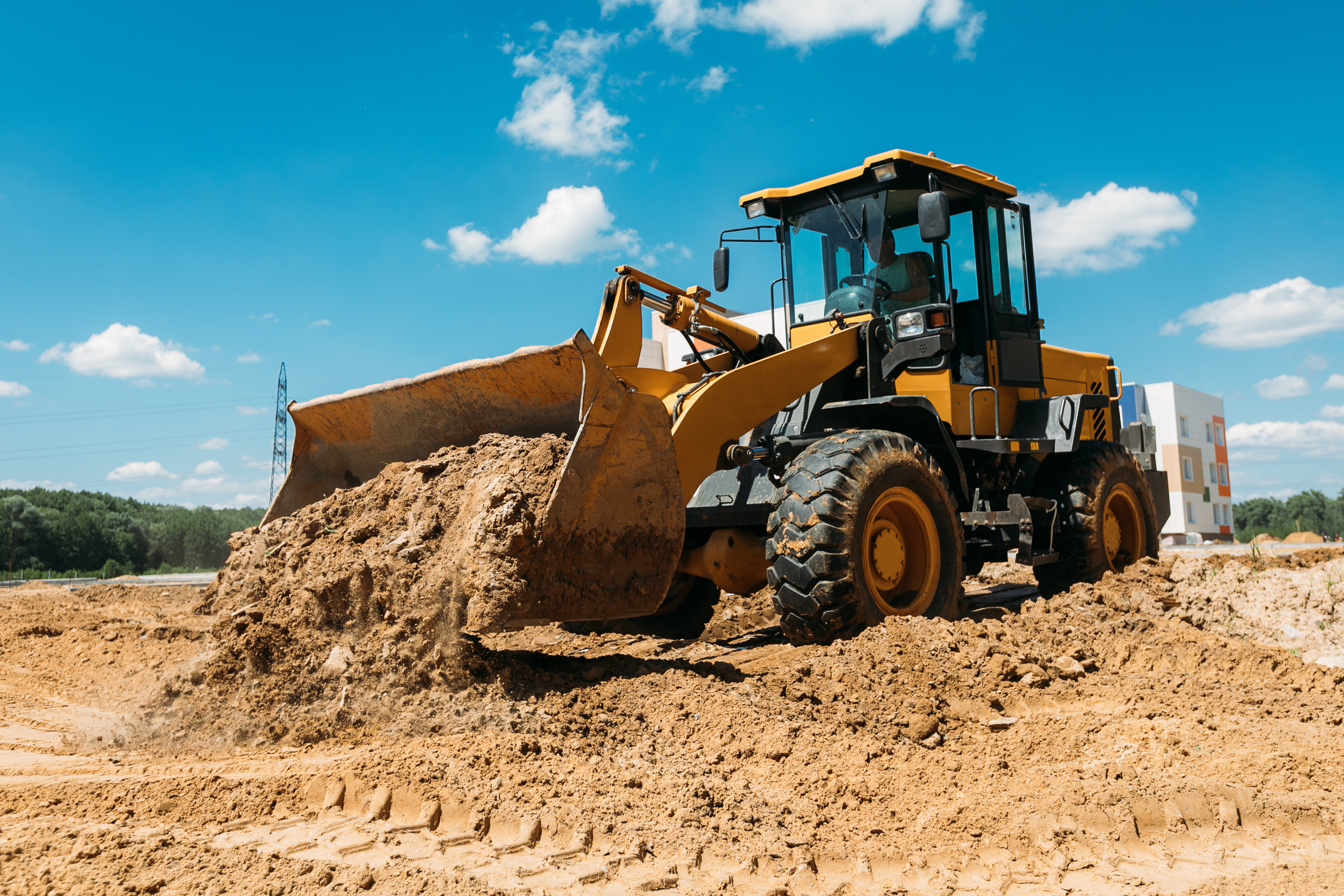
Construction runs on powerful machines, and those machines rely on hydraulic systems to lift, push, crush, pave, and haul. From bulldozers to rock crushers, it all depends on components that can handle the heat, the dirt, and the pressure. Let’s break down where hydraulics show up on the job site, the challenges these applications face, the types of components that keep things moving, and how Brennan supports this industry.
Brennan Industries Expands into Australia with the Acquisition of Aussie Adaptors & Hydraulics P/L
CLEVELAND, Ohio, August 18, 2025 - Brennan Industries, a global leader in hydraulic fittings, adapters, and accessories, is continuing its growth with the acquisition of Aussie Adaptors & Hydraulics P/L, a respected Australian supplier of specialized hydraulic solutions.
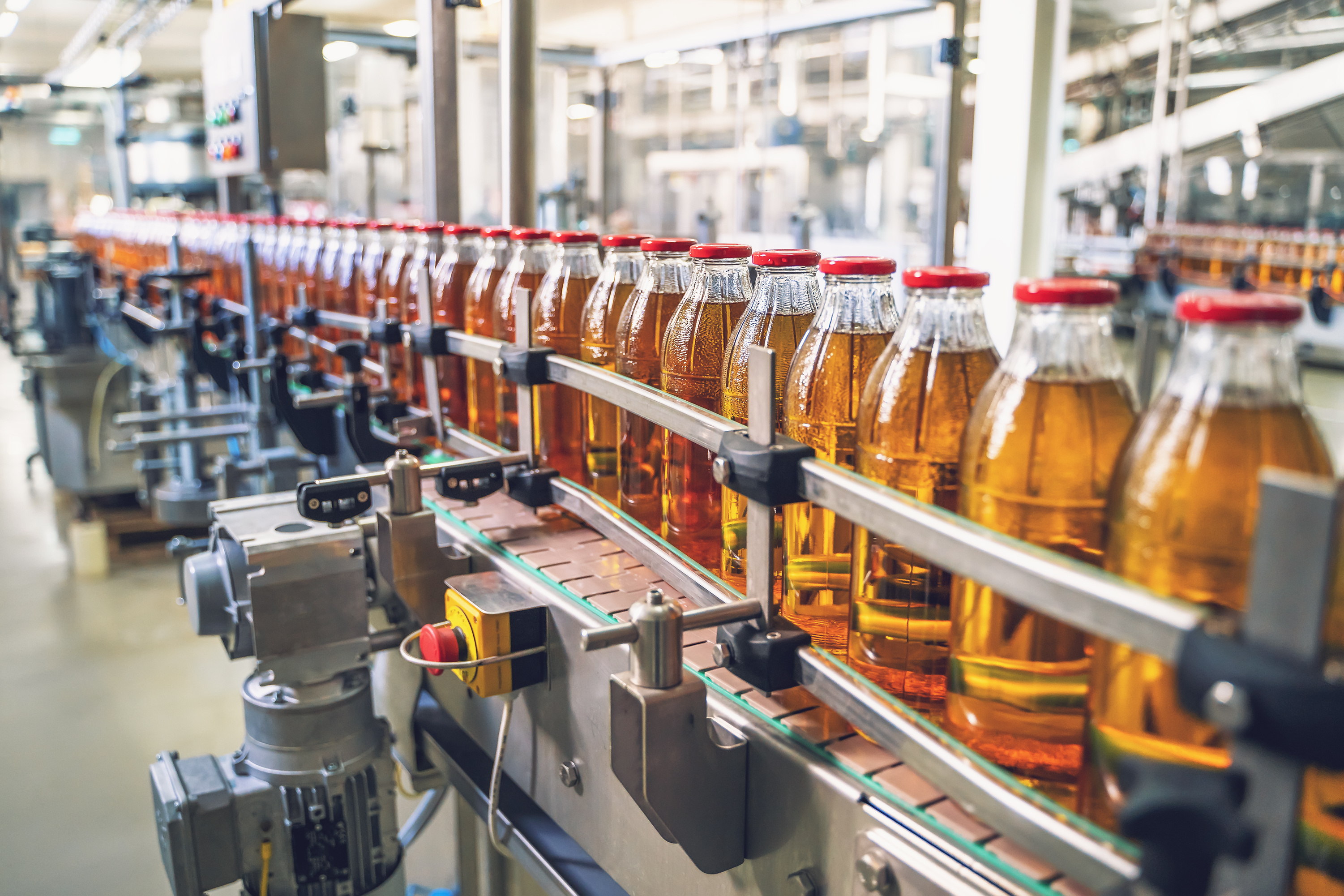
Whether you’re sipping on a soda or grabbing a quick snack, the flow of food and beverage products to your table relies on complex machinery and components working behind the scenes. From bottle & can filling machines to food packaging equipment, the food and beverage industry depends on reliable hydraulic and pneumatic systems to keep production moving smoothly. In this blog, we’ll explore key applications and essential products used throughout food and beverage manufacturing, and how Brennan supports this vital industry with durable, innovative solutions designed to meet its unique challenges.
When you pick up an apple or a head of lettuce at the grocery store, it’s easy to overlook the complex network of machines and systems that helped get it there. Behind every harvest and every shipment is a chain of hardworking agricultural equipment, each relying on tough, high-performance components to do the job. In this blog, we’ll explore key agricultural applications, the role of hydraulics and fluid power in each, and how Brennan supports this industry by providing reliable solutions that keep things flowing from field to fork.
Hydraulic and Gas Connections: Upstream Applications in the Oil & Gas Industry
When it comes to the oil and gas industry, many of us may recall the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. This incident doesn’t just highlight the dangers of offshore drilling, it also shows how important safety equipment and dependable technology really are. Hydraulic and instrumentation components help manage the immense pressures and challenges of drilling operations. Just as the crew relied on their gear to weather the storm, today’s oil and gas professionals depend on high-quality hydraulic components to facilitate seamless operations and safeguard against potential disasters. In this blog, we will explore the key upstream applications in the on-shore and off-shore sectors of the oil and gas industry and how hydraulic and instrumentation parts and components keep the industry running smoothly.
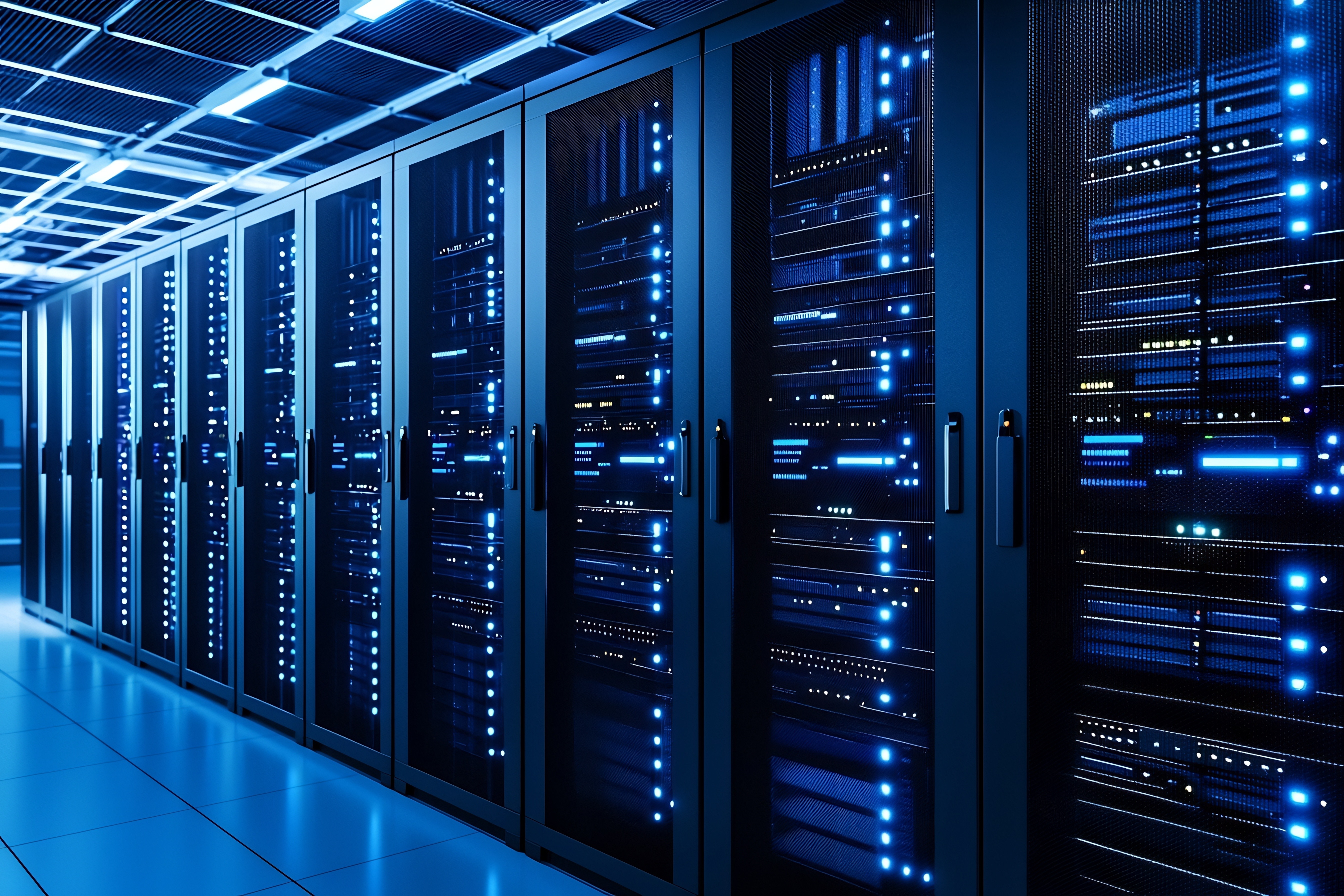
Have you ever wondered how your AI assistant effortlessly handles complex tasks? Behind every seamless interaction is an extensive network of data centers filled with thousands of servers dedicated to artificial intelligence and machine learning. These enormous facilities, often spanning millions of square feet, contain densely arranged servers and high-powered GPUs. Under intense workloads, this equipment generates significant heat. As the demand for AI grows, effective cable management and advanced cooling systems become increasingly critical. Without these measures, data centers can face overheating, reduced efficiency, and costly interruptions.
CLEVELAND, OH – March 2025 – As industries worldwide push for more sustainable practices, Brennan Industries (Brennan) is taking measurable steps to minimize its environmental impact while maintaining the highest standards of quality and reliability.
Industry-wide, sustainability has become a critical focus following the 2021 launch of the London Declaration, ISO’s Climate Commitment, which outlines the global push for climate-conscious business practices such as carbon neutral ‘net zero’ leading up to 2050. This shift is already influencing supply chain decisions, industry certifications, and how manufacturers engage with partners and customers.
Instrumentation Fittings, Valves, and Accessories for the Medical and Life Science Industry
The life science market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.28% from 2024 to 2033 (BioSpace). As a result, critical gas and fluid systems are essential to support medical device manufacturing and sustain this growth. In this blog, we’ll discuss key applications, essential products within those applications, and how Brennan contributes to the efficiency and safety of these life-saving technologies.
Brennan Industries Acquires Coterflex Industrial, Expanding Product Offerings and Market Reach
CLEVELAND, Ohio, November 19, 2024 – Brennan Industries, a leading manufacturer and distributor of hydraulic and fluid connector products, is pleased to announce the acquisition of Coterflex Industrial, a renowned Brazilian manufacturer of specialized industrial solutions. This strategic acquisition aligns with Brennan's commitment to enhancing its product portfolio and delivering innovative solutions to its customers.
Coterflex Industrial, known for its expertise in custom manufacturing and a diverse range of industrial applications, will bolster Brennan's capabilities in meeting the evolving needs of its clientele across various sectors, including aerospace, automotive, and energy. With this acquisition, Brennan aims to enhance operational efficiencies and expand its geographic footprint.
SOLON, Ohio, August 23, 2024 – Brennan Industries, Inc. (Brennan) was recognized as a 2024 NorthCoast 99 winner by ERC, in Northeast Ohio. This prestigious award highlights Brennan's commitment to creating an exceptional work environment that fosters innovation, growth, and employee well-being.
“We are honored to be recognized as a NorthCoast 99 winner,” said Angela Sebesy, Global Vice President of Human Resources. “It underscores our dedication to building a workplace where top talent can thrive and contribute to our ongoing success."
SOLON, Ohio, August 12, 2024 – Brennan Industries, Inc. (Brennan) announces a week dedicated to promoting workplace safety and employee well-being from August 12th to August 16th in collaboration with OSHA’s Safe and Sound Week. This year, Safe and Sound Week aligns with National Wellness Month, allowing Brennan to emphasize commitment to overall wellness.
“Safety and wellness go hand in hand, and at Brennan. We continuously strive to create an environment where our employees feel safe and supported,” said Rob Ward, VP of Operations at Brennan. “Beyond Safe and Sound Week, we incorporate these initiatives year-round across all our locations, implementing the value of physical and mental well-being into our culture.”
Although the upcoming Safe and Sound Week is nationally focused, Brennan emphasizes safety at its global locations throughout the year. Last quarter, Brennan’s facility in Mississauga, Canada, participated in a program offered through WSIB for Health and Safety Excellence, where employees implemented five new health and safety procedures, including first aid and safety communication protocols. Additionally, at Brennan’s newest facility in Querétaro, Mexico, management is completing a study of operations as required by the government, reinforcing the company's commitment to safety and compliance globally.
Subscribe to Blog Notifications
Keep up to date with the latest from the Brennan Blog by subscribing to blog notifications below. Every month we will send you a brief digest of the latest posts with a link where you can read more.









.png)

.png)
.png)